On 12 January 2019, our Training Director, Professor Joel Lee, published a blog post on the Kluwer Mediation Blog entitled "A Neuro-Linguist's Toolbox - Rapport: Metaphors". His blog post is reproduced in full below.
A Brief Recap
This entry is an ongoing series focused on using Neuro-Linguistic Programming in our practice of amicable dispute resolution. For ease of reference and the convenience of readers, I will list in this and subsequent entries the series and links to it.
1. A Neuro-Linguist’s Toolbox – A Starting Point and Building Rapport
2. A Neuro-Linguist’s Toolbox – Rapport: Non-Verbal Behaviours
3. A Neuro-Linguist’s Toolbox – Rapport: Representational Systems (Part 1)
4. A Neuro-Linguist’s Toolbox – Rapport: Representational Systems (Part 2)
5. A Neuro-Linguist’s Toolbox – Rapport: Values
In the previous instalments in this series, we explored building rapport by pacing non-verbal behaviours, representational systems and values. In the sixth of this series, I would like to focus on pacing something as deep as, if not deeper than, values; metaphors.
Metaphors
The followers of this series who have read parts 3 & 4 will remember that visual, auditory or kinesthetic predicates are often taken to be metaphorical expressions when in fact, they function quite literally. When someone says “I see what you are saying”, they are actually looking at an internal image/movie that represents what they have constructed from what you have said. The same is true in the auditory or kinesthetic representational systems when they say “That sounds sensible” or “That feels right” respectively.
That these (often assumed to be) metaphorical expressions are literal does not mean that our brains are literal. The thinking in cognitive psychology, narrative theory and neuroscience suggest that the human brains function associatively. Put simply, things, ideas and concepts are connected to and associated with other things, ideas and concepts.
How Connections Occur
These connections occur in one of two ways. The first is a cause and effect, i.e. X leads to Y. For example, someone might say “Exercising makes me strong”. This connection is quite straightforward and will probably have few people disagree with them. However, a cause and effect statement like “Being a man makes me an angry and aggressive person” is probably a connection that will take a few more mental leaps for others to get. And even when they do get it, they may not agree. The point however is that this cause and effect connection is very real for the person making the statement. In other words, it is a belief.
Perhaps we will discuss beliefs in a subsequent instalment in this series. For this instalment, I would like to focus on the second connection. This is the equating of 2 things, ideas or concepts with another, i.e. X = Y. In NLP, this is referred to as a complex equivalent. For example, “My love is like a house on fire” or “Life is an uphill battle” or “In business, it’s a jungle out there”. In each of these examples, you will see that two things are equated; “Love” with “House on Fire”, “Life” with “Uphill Battle", and the “Business” context with “Jungle”. These are also all beliefs but expressed metaphorically.
At this point, it is useful to point out that while in language, there are technical differences between analogies, similes and metaphors, it is sufficient for our purpose to take a metaphor to be any equivalence between two things, ideas or concepts.
Let's play!
Take the time to complete the following equivalences (If it is easier, one can exclude the word “like”):
Love is like…
Life is like…
Conflict is like…
Negotiation is like…
Mediation is like…
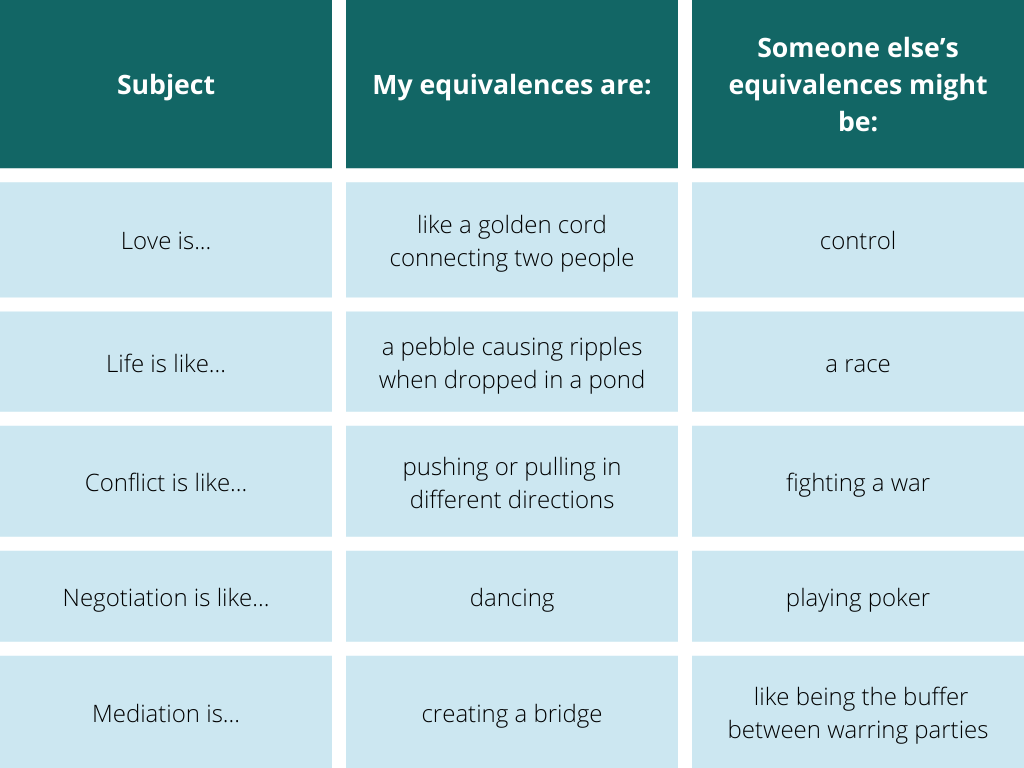
Take a moment to compare your list of equivalences with mine and then with the third list. Are there any that are the same? Or, while not exactly the same, have a similar intent or spirit? Perhaps diametrically opposed?
What do our Metaphors mean?
These equivalences or metaphors are how we perceive and interact with the world.
For each metaphor, there are values and beliefs associated with that metaphor. Someone who sees conflict as fighting a war may believe that in a conflict, there must be a winner or a loser. That there will be casualties or collateral damage and that having superior fire power will determine the outcome.
This person will see the world very differently from the person who sees conflict as growth who does not necessarily think that there is a winner or loser. S/he may consider that conflict means helping each other learn.
And of course, these metaphors affect our behaviours as we interact with the world.
Therefore, learning to identify the metaphors people hold in various contexts can give us significant insight into their mindset and their behaviours. And this can be done conversationally by simply asking them in relation to any particular thing “What’s that like for you?” So, if we were talking about conflict, you could ask me, “What’s conflict like for you?”
Building Rapport
Sometimes, the metaphor will just pop straight out. Other times, it may be “hidden” within various things they say. This is when listening skills come in very useful. Metaphors surface in the things people say. For example, “We need to strengthen our defenses” or “We are fighting a war against ignorance”. If these are statements that stem from a particular metaphorical view of the world, what would that metaphor be? For example, “strengthening defenses” could come from a metaphor of war or battle. It could invoke feelings of being under siege or losing ground. And the metaphor itself implies that they see that particular context as a win-lose situation.
Once we can hear and identify these metaphors, the issue isn’t whether we agree with them or see them the same way. We can use them to build rapport by pacing their reality. This can be done by using the same terms, or speaking to their values or beliefs. For example, with someone who sees conflict as a battle, we can use metaphors of war to connect with them. This will build rapport with them at a fairly deep level.
How do we practice this?
At this point, it is important to point out that because metaphors shade into the content of what we do, it may not always be helpful to only pace their metaphorical world view. Doing this will only tap into a metaphor that may not be conducive to our purposes. For example, if we were negotiating a dispute and our counterpart saw negotiation as a battle, buying into that win-lose paradigm would not be helpful, especially if your metaphor is an incompatible one.
The key thing to remember is that for the purposes of building rapport, we must first pace their model of the world and understand their reality. Once we have rapport, we can then lead them in a more useful or conducive direction. In terms of metaphor work, this could mean reframing their metaphor or utilizing it or evolving it. Discussing these interventions is outside the scope of this entry and may be the subject of a future instalment in this series.
That brings us to the end of this entry and also concludes the section on building rapport. It is hoped that this section has provided readers with more tools in their toolbox (you should be noticing the metaphor here) to connect with others in the contexts you operate within and that readers have found these tools helpful and empowering.
To learn more about how Neuro-Linguistic Programming can help you, join us on the journey towards solving "The People Puzzle" - Prof Joel's flagship NLP training series. Obtain the blueprint to achieve greater self-awareness, enhance communication with others, and connect with people more effectively.
Unlock the People Puzzle today! 👉 https://peacemakers.sg/the-people-puzzle/

